Apple and Jaguar Land Rover blamed the Chinese economy for their recent financial results. The truth is probably more complex. What factors are affecting affecting Apple and Jaguar Land Rover that aren’t directly related to the Chinese economy?
The reality is that Apple and Jaguar Land Rover are being buffeted by very different forces, some of which are their own making.
Apple
China is a unique mobile environment and in some ways it mirrors the hopes (and fears) for the internet in the late 1990s. Oracle and Sun Microsystems spent a lot of time during the dot com boom developing technologies that would allow applications to run on the web. Enterprise software sudden had a user experience that could be accessed via a web browser. Java allowed applications to be downloaded and run as needed. Netscape had a vision of the internet replicating the operating system as a layer that would run applications. Microsoft also realised this which was why they developed Internet Explorer, integrated it into Windows and killed off Netscape. The Judge Jackson trial happened and that was the start of the modern tech sector allowing Google and Apple to rise.
Move forwards two decades and most computing is now done on mobile devices. In China, WeChat have managed to achieve what Netscape envisioned. Their app as a gateway to as many services as a consumer would need including a plethora of mini applications. It doesn’t suffer the problems that native web apps have had in terms of sluggish user experiences. In addition, WeChat has invested in a range of high-performing start-ups to built a keiretsu of businesses from cab services, e-commerce, property companies and even robotics. In the meanwhile Tencent who own WeChat have a range of consumer and business services as well.
What this means for Apple is that many of its advantages in other markets are negated in China. The OS or even performance of a smartphone doesn’t matter that much, so long as it can run WeChat and a couple of other apps. The look and feel of the app is pretty much the same regardless of the phone OS. Continuity: where the iPhone and a Mac hand-off seamlessly to each other doesn’t matter that much if many consumers use their smartphone for all their personal computing needs.
This has been the case for a few years now in China – but Apple haven’t found a way around it.
As for phone industrial design – Apple lifted the game in manufacturing capability by introducing new machines and new ideas. To make the iPhone 5, Apple helped its suppliers buy thousands of CNC machines. This grew the manufacturers capability to supply and the amount of pre-owned machines that eventually came on the marketplace. It meant that other manufacturers have managed to make much better phone designs much faster.
That meant Chinese consumers can buy phones that are indistinguishable from an iPhone if you ignore the logo and function the same because of China’s app eco-system. Again this has been the same for a few years and has accelerated due to the nature of the dominant smartphone form factor. The second iteration of the iPhone X form factor is what really changed things. The phones were different to what has come before, but they weren’t demonstrably better. They were also more expensive.
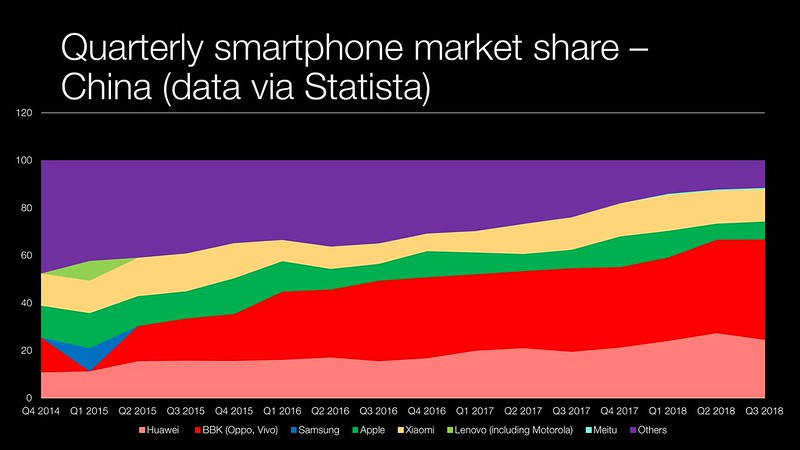
In the mean time Huawei and others have continued to make progress, particularly in product design and camera technology – the two areas where Apple led year-on-year. Huawei devices can be expensive for what they are, but they gave domestic manufacturers ‘brand permission’ in the eyes of many Chinese consumers to be as good as the foreigners.
This wasn’t helped by Samsung’s missteps in the Chinese market that started with the global recall of the Samsung Galaxy Note7 battery recall. Samsung hasn’t managed to make that gap back up and seems to make marketing missteps regularly such as its recent tie-in with the ‘fake’ Supreme brand holder China. If you’re a Chinese consumer the additional value or status that you used to see in foreign handset brands is now diminished. This seems to be a wider theme as domestic brands are also making similar gains in market share compared to foreign FMCG brands. Although there are also exceptions like baby formula.
Domestic brands have done a good job marketing themselves. BBK in particular are very interesting. Whilst Huawei makes lots of noise and bluster at how big they are, BBK creeps up. It has a number of brands in China and abroad OnePlus, Oppo, Vivo and RealMe going after particular segments. The brands are focused but run separately like companies in their own right. Apple’s marketing riffs on its global marketing (though it did a great Chinese New Year themed ad last year). This reinforces the perceived common view that foreign businesses are full of hubris and don’t sufficiently localise for China. Apple’s recent pricing strategy in a market where this is so little to show in value provided looks like the epitome of hubris.
Finally, there has been a massive amount of consolidation of brands in the China smartphone market over the past four years. That provides for scale in terms of logistics, supply chain, design, component sourcing and marketing.
Jaguar Land Rover
If we move to the automotive sector and look at Jaguar Land Rover – their problems in China look self inflicted. China’s car market has declined for the first time in 20 years. But it seems to have mostly affected brands like Hyundai rather than prestige brands like Mercedes Benz or BMW. The reasons why aren’t immediately apparent. Yes diesel cars are less popular, but BMW, Audi and Mercedes make diesel cars.
Jaguar Land Rover aren’t the only foreign brand suffering: Toyota has had problems in China since the last round of strong anti-Japanese sentiment exploded in 2012.
More information
Why Does WeChat Block Competitors, While Facebook Doesn’t? | Walk The Chat
Apple’s China Problem | Stratechery
Samsung recalls Galaxy Note 7 worldwide due to exploding battery fears | The Verge
Samsung angers hypebeasts by partnering with fake Supreme brand in China | The Verge
Fake News: Samsung China’s Deal With Supreme “Knock-off” Spurs Drama | Jing Daily
Chinese car sales fall for first time in more than 20 years | World news | The Guardian