Video conferencing
A couple of interesting artifacts that I found online and wanted to share with y’all.First up, video conferencing, why is it so crap and what are you going to do about it?
Ok, we’ve had video online, we’re now living in an age of pretty much ubiquitous broadband, why do we stop with using our VoIP client of choice and use video instead.Well there is the network side of things: IP networks provide a ‘best effort’ service so the signal may be come degraded. All the pixels will get to the other end eventually but they won’t get there in the right order and the latency of the signal will depend on the slowest part of network travel that they have to make through the internet ‘cloud’ no matter what kind of pipe you have between you and your local telephone exchange, wireless hub or cable television outfit. Look at video streaming, it has errors and flaws in its signal even on my 2MB pipe AND the signal is buffered to smooth out these glitches like a CD player. With real-time interactive video conversations that is not a technical option.
Also you may not want to have the person see you as well as speak to you, imagine if you have a bad hair day or want to lie?
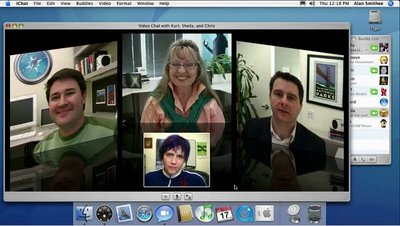
The third factor is a much more basic human system and the best way of illustrating it is by looking at the picture above. Notice how you don’t have eye contact with the people that you have a conference with because the camera’s perspective is slightly different to the view you would have if it were a real-world conversation. Notice how the men on the left and right are looking above their screens and the ladies are looking below, this is just enough for you to notice and process at a low level. It doesn’t feel natural, the conversation won’t flow as well as a real-world sit down would because the eye contact feels wrong.
This is why video conferencing can feel so wrong, even Apple’s attempt at correcting it with a small mirror picture (the one at the bottom) to see how you look to the callers feels wrong.
Historically the way to do that is to have the difference between camera angle and the viewing angle of the screen as small as possible. This was achieved by using big TV screens with a camera on top and the participant perched at the end of a big conference table at the other end of the room. That’s why big oil companies and George Bush love video conferencing but you’re not likely to see it adopted en masse in UK homes soon.
Its also not exactly the most elegant solution, which the reason why I was really intrigued by this Apple patent which I saw courtesy of those nice people at AppleInsider.
Imagine where the screen viewing area was the camera with camera elements squeezed in between the pixels on your LCD. The back-light would provide the ambient light required for the picture, you an have eye contact with whoever you are speaking with without living in a mansion and having a conference table the size of a small yacht.
In theory this principle would also work with on mobile screens (at a lower quality-level), televisions etc. On the scary side it would also allow the omni-present two-way tele screens for surveillance like Orwell’s Nineteen Eighty-Four. More content here.
Web 2.0 and the Enterprise
News.com have an interesting article Web 2.0 meets the enterprise how companies like IBM and Visible Path are using technologies like social networking, RSS feeds and wikis to help large companies build IT systems. News.com make a big show of how these ‘consumer’ (their word, not mine) technologies are changing the enterprise software landscape.In addition, Forrester sent out an email newletter talking about how service-orientated architecture (SOA) (simply put: enterprise-grade web 2.0-type technologies) are having an accelerated take-up with happy IT directors to be found everywhere.
The truth is more complex than the News.com story about how the kids are showing big business the way, the process is much more complex.
AJAX is generally a hard thing to do well so it is interesting that Michael Robertson is selling AJAX-based web services through ajaxLaunch and looking to use AJAX as a way of providing applications and widgets on top of an OS. Its an interesting take from a business head on all the utopian dreams such as the network computing meme or Netscape’s ‘the browser is the OS’-hype back in the day and an ideal way for novices to get web 2.0 see his ‘everything is moving to the cloud’ keynote here which also has a good product demo (RealPlaya required).
Nice definition of what AJAX means to marketing people – ‘rich web applications right to your computer’.
