I initially looked at app constellations back in 2014, when Fred Wilson put a name to the the phenomena. And every two years or so I have gone back and looked at a number of major internet companies to see how many different types of apps that they had in play.
I originally selected the companies back in 2014 because I felt that they represented the largest and best of their ilk. It skews Asian because the west can be viewed as one eco-system represented by Google, Facebook and Microsoft.
China is an enclosed eco-system; though Microsoft is actively engaged in the app eco-system there. I chose Tencent and NetEase as being my Chinese bellwethers. DaumKakao and Naver were representative of the Korean eco-system which blends highly-used domestic services with western platforms. Finally LINE of Japan (a subsidiary of Korean company Naver) provided a similar bellwether of the hybrid Japanese eco-system which mirrors Korea.
App constellations survey methodology
For the sake of convenience I have compared the contents of Apple’s mobile app store for each of the companies. While most of the internet companies have some Android-only or iOS-only apps; the iOS app store is still a good indicator of their app activity.
I stayed true to the definition of app constellations in terms of deciding what kind of app should go in.
I manually assessed each app, rather than relying on the category that the app had been submitted into. Tencent and Netease, had a number of mobile utilities that aided discussion and kept players updated on their favourite game. These didn’t fit within the definition.
Changes in the environment
Since 2016, a couple of things have changed:
- Apple had a purge of apps that didn’t support 64 bit processing
- They moved away from supporting the app store within iTunes application and on the web; to within the app store on the device
2018 marks over a decade of mobile apps in the Apple store. Many of the major players have delisted almost as many Android and iOS apps as they currently have in the store. This happens for a number of reasons:
- The app was serving a purpose for a fixed time
- It is an application that has fallen so far out of favour that it is no longer worth maintaining
- The code base no longer meets Apple’s or Google’s minimum standards
Data analysis
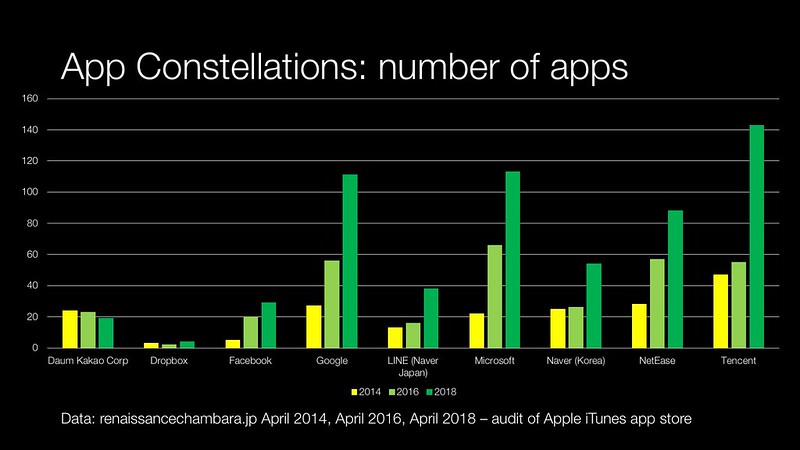
I started off by looking at the number of apps. In terms of app constellations: Tencent, Microsoft and Google were clear winners.
Both Microsoft and Google’s growth has been driven by ‘experimental’ apps that they have put out in the public for their own reasons and enterprise focused apps.
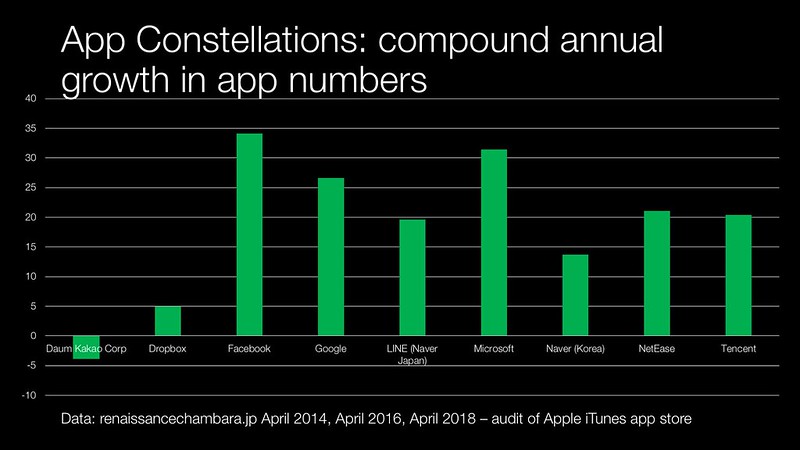
But it was quickly apparent to me that the number of apps developed were only part of the story. What about the rate of change in numbers of apps developed? This would be indicative of the rate of change in moving to mobile. Here both Facebook and Microsoft’s pivot became immediately apparent. The Asian companies looked less impressive as they had been able to keep steady in their focus on mobile.
All of this growth in the number of apps developed by major internet companies is all the more remarkable when you consider the following:
- In mature markets consumers are not really downloading new apps
- They are sticking with a few in terms of regular usage. Many of the apps on their phones don’t get used
Notes on a few of the companies in terms of their app constellations
- Daum Kakao – notable for being the only company who I looked at who had a decline in the number of applications versus 2016. A lot of this seems to be in service consolidation of both Daum and Kakao to remove duplications or non-core services. It is the Daum brand that has taken the biggest impact. This is understandable, since Daum struggled on the move to smartphones and Kakao is a mobile-first brand.
- Dropbox – the growth in apps has been down to the larger business acquisition strategy at Dropbox. I don’t expect further growth like what we have seen with Facebook’s pivot to mobile
- Facebook – Facebook’s pivot to mobile was one of the reason why I decided to look at compound annual growth rate as well as the size of app constellation in terms of app numbers. In terms of raw app ‘SKUs’ Facebook is dwarfed by most of the other companies that I have looked at. It is only by looking at the growth in apps developed where one can really see their move to mobile
- Netease – was interesting for its focus in a couple of areas. Like other Asian internet companies, education was a big target area, but Netease went into it with major commitment. Both NetEase and Tencent were big in magazine and book apps as well. I think this is down to the fact that ‘traditional’ web surfing is harder to do with (at the moment) when URLs are written in western script and numbers.
- Tencent – the raw app numbers beggars belief. There are a number of reasons for this. Like NetEase, Tencent has a lot of apps solely optimised for the iPad and a separate iPhone app. There are free and paid-for product variants. Lastly Tencent will have four or five apps competing in a given category like streaming music which seems insane. Only time will tell if Tencent is spreading itself too thin; like when Yahoo! was described Brad Garlinghouse’s Peanut Butter Manifesto
More information
Jargon watch: app constellation – back in 2014 when I wrote this post, it still took me the best part of a week to research and describe each of the apps in the main eco-systems. It would take me much longer today due to the growth in apps
Peanut Buttergate – analysis of Garlinghouse’s original memo about Yahoo! from back in 2006