There are a number of people who have done great trends / predictions for 2018. I thought that I would focus on what I would like to see across three trends: innovation stuckness, lean web design, machine learning ethical considerations, buffer bloat and redefining what a technology start-up is.
Smartphones are stuck in a period of innovation stuckness. It is becoming increasingly difficult to justify upgrades to your handset. This has had knock-on effects to mobile networks. In markets where subsidised handsets are the norm like the UK we’re seeing that SIM-only contracts are becoming the norm.
Apple is trying to innovate its way out of this problem with its work on augmented reality interaction. Consumer media consumption will take a good while to catch up.
Smartphone cameras are as good as consumers need (at the moment). Displays are now good enough that improvements look indistinguishable. They are also large enough for you to watch Amazon Prime or Netflix during a commute. Mobile wallets are merely a back-up in case one leaves your wallet at home.
Whilst the app names have changed, much of the smartphone usage now is for the same things I used a Nokia or Palm smartphone ten years ago:
- Alarm clock
- Web surfing
- Entertainment
- Media playback
- Communications
I hope that we start to see smartphones going back to the future and looking at different form factors. My iPhone would be much more useful as a productive device if it was available in a similar form factor to the old Nokia communicator. Different form factors of devices for different users. Gamers would benefit from better controls a la the Nokia nGage.
Interfaces can make better use of haptic feedback, and be designed to take advantage of more hardware-optimised devices.
Innovation isn’t only the responsibility of app developers and phone makers. What about a modern 4G version of ‘Enhanced Full Rate’ on GSM (GSM-EFR) ‘hi-fi voice calls’. UK operator One2One launched GSM-EFR on 2G networks in the late 1990s as part of their Precept tariffs, but I haven’t seen any other carrier try to do a similar thing since. Why not? I suspect part of the problem is that ‘innovation’ in your average mobile network provider now is testing vendor products in a lab to ensure they work properly on their network.
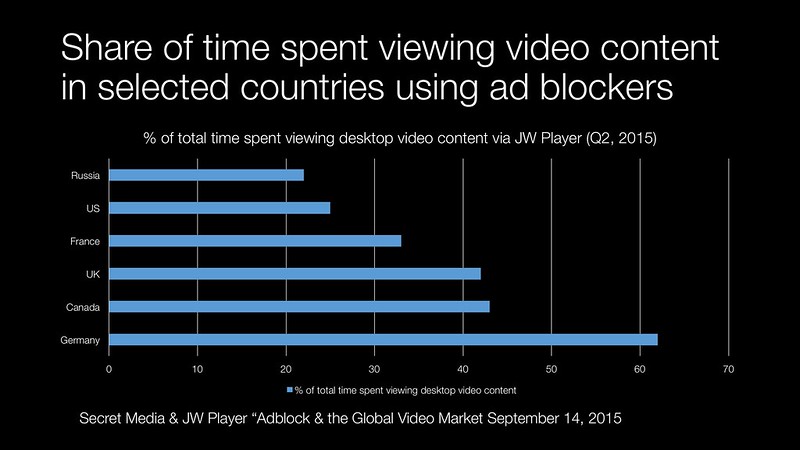
The web has developed a digital equivalent of clogged arteries. Part of this is down to buffer bloat and a lack of lean web design approach. Unfortunately the mobile web has not brought a clean slate approach but hacked together adaptations. A bigger issue is the layers of advertising technology trackers, analytics and assorted chunks of Javascript. Ad tech hammers page load time and responsiveness.
We’ve seen Apple and Mozilla try to redesign their browser technology to slow down or stimmy ad technology. Consumers are adopting ad blockers to try and improve their own web experience.
There needs to be a collective reset button. I am not sure if we see a resurgence of the paid web or a kinder lighter footprint in advertising technology. Otherwise we have an unending conflict between the media industry and the rest of us.
The debate around machine learning in 2017 highlighted a Black Mirroresque dystopia awaiting us. The good news is that we tend to overestimate technology’s impact in the short term. In the long term the impact tends to meet our expectations all be in a more banal way.
Part of the current problem around machine learning is that Silicon Valley seems to only consider technology rather than the consequences of potential use cases. This needs to change, unfortunately the people in charge of technology companies are the least capable people to achieve it. We need a kinder more holistic roadmap. Legislation and regulation will be far too late to the party. We won’t be able to stop technological progress, but we can influence the way its used.
Lying in bed ill over the Christmas period, I read that crypto currency mining currently required as much energy as Bahrain. By the end of 2018, it will require as much energy as Italy. That is insane.
Apart from speculation and buying products on the dark web what is the killer app for crypto currencies? Why is worth the energy overhead? Steve Jobs focused on computing power per watt as part of his vision for laptops and moving the Mac range to Intel. Part of the move to the cloud was about making computing more efficient for businesses and providing computing power over the network for consumers on ‘low power’ mobile devices. Yet almost a decade and a half later, the hottest thing in technology is a grossly energy inefficient process.
We are starting to see regulators in Korea and China step in to regulate the market and energy supply to miners, but western economies need to look at this. And I haven’t even got on to the ICO (intial coin offering) as Ponzi scheme…
If you substitute the words ‘fax machine’ or ‘call centre’ for app would Uber, Deliveroo etc be considered as technology companies? I suspect that the answer is no. A company may use a lot of technology – it happens a lot these days. But that doesn’t make Capita, Mastercard or Goldman Sachs a technology company, lets apply a bit of critical thinking. I wouldn’t mind, but this same mistake was made in the late 1990s during the dot com boom.
Many companies including Enron were ‘repackaged’ by management, venture capitalists, investment banks and consultancies (cough, cough McKinsey) as asset-light technology driven businesses aka ‘an internet company’. It didn’t work out well last time. It won’t this time either.
More information
Enhanced full rate (GSM) – Wikipedia
Bitcoin Energy Consumption Index | Digiconomist
Setback for Uber as European court advised to treat it as transport firm | Reuters
Other trends reports
Fjord: 2018 Fjord Trends
iProspect: Future Focus 2018: The New Machine Rules
Isobar: Augmented Humanity: Isobar Trends Report 2018
J. Walter Thompson Innovation Group: The Future 100
Ogilvy & Mather: Key Digital Trends for 2018 – Whatley and Manson are doing webinar presentations this week if you want to catch them
Campaign Asia did a nice precise of them all
Past prediction stuff that I’ve done
2016: crystal ball gazing, how did I do? | renaissance chambara
2016: just where is it all going? | renaissance chambara
2015: crystal ball gazing, how did I do? | renaissance chambara
2015: just where is it all going? | renaissance chambara
2014: crystal ball gazing, how did I do? | renaissance chambara
2014: just where is it all going? | renaissance chambara
Crystal ball-gazing: 2013 how did I do? | renaissance chambara
2013: just where is it all going? | renaissance chambara
Crystal ball-gazing: 2012 how did I do? | renaissance chambara
2012: just where is digital going? | renaissance chambara
Things I’d like to see in 2012 | renaissance chambara
Crystal ball-gazing: 2011 how did I do?
2010: How did I do? | renaissance chambara
2010: just where is digital going? | renaissance chambara
Predictions for 2009 | renaissance chambara