Kurt Anderson wrote an essay in Vanity Fair where he argued that product design in everything from fashion to homewares has stood still over the past two decades. It was an interesting that got me thinking about hypothetical reasons why his theory maybe true.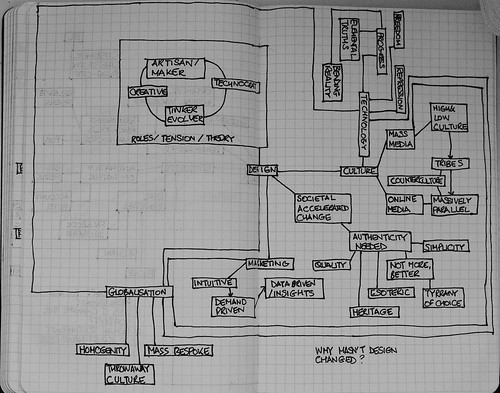
There were a number of possible factors that I came up with:
Design – product design education has gone global – design professionals now know more about product design than they ever have done before. You now have product designers who can access the same influences from all over the world from the same place. The design computerised tools haven’t changed radically from the early 1990s but they have become more pervasive. Product design and culture are inextricably linked and culture as we previously knew it has been disrupted.
Culture – The structure of culture has changed. Where the mass-media, publishers like Taschen and (often hard-to-get) style magazines or fanzines were the arbitors of the latest tribe, high and low culture trends, now Google is likely to turn up images and blogs about what whatever you want. This has meant that fashion is no longer linear in its timeline, but massively parallel: from cosplay and rockabilly to ‘rugged’ style – fashion sensibilities resonates around the world in a self-sustaining loop with more power than previously.
The pressures on culture have also changed; in the west there is no longer a sense that progress is inevitable. Even up to the 1990s with the Hubble space telescope and the Channel tunnel; big exciting things were being done and aspects of technology were interesting or exciting. You still have this; only its in China, Brazil and India. Environmental concerns and a wider anti-science movement that has gained momentum have squeezed the joy out of progress.
Societal change – seems on some levels to be going at an ever faster pace, which means that culture values things like authenticity, by looking to simpler times in the near past. Authenticity comes from:
- Simplicity
- Heritage
- Esoterism
- Quality
Globalisation – Autenticity can also be seen to be a backlash against the tyranny of choice that globalsiation has provided. Retailers in the west have created giant sheds to handle their massively expanded but similar product lines. This has promoted a homogeneity in many product lines and product design in those product categories. It has also promoted a throwaway culture: H&M clothing for instance – which is at odds with environmental concerns, particularly when you think about what goes into growing cotton. On the plus side it has also created opportunities for mass bespoke manufacture – supporting various subcultures through ecommerce and better logistics.
Marketing – finally marketing has changed from being intuitative and demand-driven to being much more data and insights driven in nature and this has affected the product development process with every aspect of it undergoing scrutiny. The key challenge is that often people don’t really know that they want, but the space for vision is now lacking.
You can find more design related content here.